What are EC2 Instance Launch Types?
Introduction
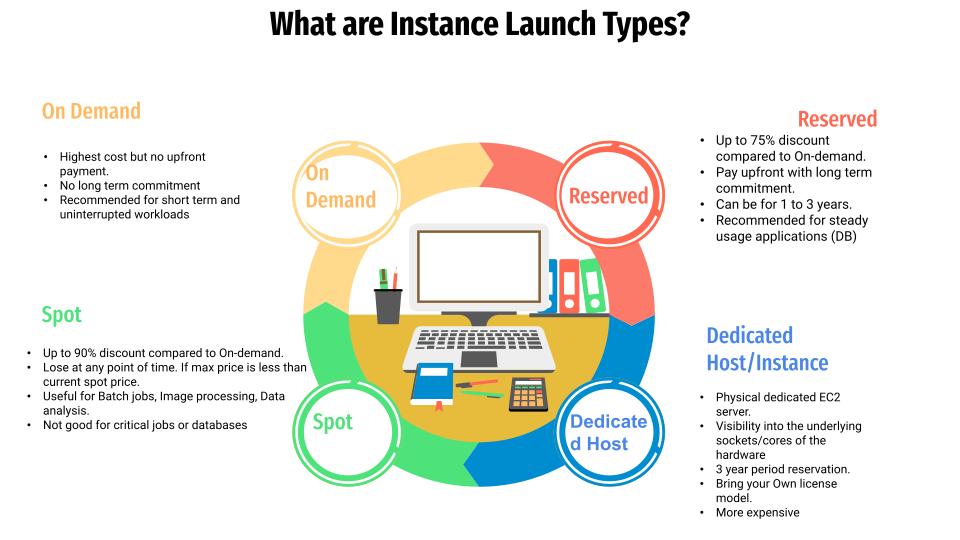
Amazon EC2 offers several instance launch types to meet different workload requirements and cost considerations. These launch types determine how you pay for your instances and the flexibility you have in managing them. Let’s explore each of these launch types and their use cases.
1. On-Demand Instances
- Description: On-Demand Instances are the most flexible option, allowing you to pay for compute capacity by the hour or second without any long-term commitments.
- Cost: They have the highest cost compared to other options but require no upfront payment.
- Commitment: There is no long-term commitment involved, making them ideal for applications with unpredictable workloads.
- Use Cases: On-Demand Instances are recommended for short-term, unpredictable, and uninterrupted workloads. They are perfect for testing and development environments where workloads can vary significantly.
2. Spot Instances
- Description: Spot Instances allow you to take advantage of unused EC2 capacity at significantly reduced prices.
- Cost: They offer up to a 90% discount compared to On-Demand prices, making them extremely cost-effective.
- Availability: However, they can be terminated at any time if the Spot price exceeds your maximum bid, so they’re best suited for flexible workloads.
- Use Cases: Spot Instances are ideal for batch jobs, image processing, big data analysis, and other tasks that can be paused and resumed without impacting business operations. They are not recommended for critical jobs or databases due to the risk of interruption.
3. Reserved Instances
- Description: Reserved Instances provide a discount on EC2 usage in exchange for committing to a specific instance type for a period of one to three years.
- Cost: They can offer up to a 75% discount compared to On-Demand prices, especially with upfront payment.
- Commitment: Reserved Instances require a long-term commitment, making them suitable for predictable workloads.
- Use Cases: These instances are recommended for steady-state applications such as databases, where you can accurately predict the needed capacity over time. By locking in capacity, you save money and ensure consistent performance for essential applications.
4. Dedicated Hosts/Instances
- Description: Dedicated Hosts provide physical EC2 servers exclusively for your use. They offer visibility into the underlying hardware, including sockets and cores.
- Cost: Dedicated Hosts are more expensive but necessary for certain regulatory or compliance needs.
- Commitment: They typically involve a 3-year reservation period, allowing you to bring your own licenses for software that is licensed per socket or per core.
- Use Cases: Dedicated Hosts are suitable for workloads requiring isolation from other customers’ workloads for compliance reasons. They are also ideal for using existing server-bound software licenses. However, they come with a higher cost due to their dedicated nature.
Conclusion
In summary, Amazon EC2 provides a range of instance launch types to fit different workload needs and budget considerations:
- On-Demand Instances offer maximum flexibility and no commitment, suitable for unpredictable workloads.
- Spot Instances provide the lowest cost but come with the risk of interruption, making them ideal for flexible and non-critical workloads.
- Reserved Instances offer significant savings for predictable, long-term workloads.
- Dedicated Hosts cater to specialized needs requiring hardware isolation and licensing control.
By understanding each launch type’s characteristics and use cases, you can make informed decisions that optimize both performance and cost for your applications on AWS.